August 9th, 2013 by Bradley Huffaker
We recently released a visualization at http://www.caida.org/research/topology/as_core_network/ that represents our macroscopic snapshots of IPv4 and IPv6 Internet topology samples captured in 2013. The plots illustrate both the extensive geographical scope as well as rich interconnectivity of nodes participating in the global Internet routing system.

IPv4 and IPv6 AS Core Graph, Jan 2013
This AS core visualization addresses one of CAIDA’s topology mapping project goals is to develop techniques to illustrate structural relationships and depict critical components of the Internet infrastructure. These IPv4 and IPv6 graphs show the relative growth of the two Internet topologies, and in particular the steady continued growth of the IPv6 topology. Although both IPv4 and IPv6 topologies experienced a lot of churn, the net change in number of ASes was 3,290 (10.7%) in our IPv4 graph and 495 (25.7%) in our IPv6 graph.
In order to improve our AS Core visualization over previous years, this year we made two major refinements to our graphing methodology, including how we rank individual ASes. First, we now rank ASes based on their transit degree rather then their outdegree. Second, we now infer links across Internet eXchange (IX) point address space, rather than considering the IX itself a node to which various ISPs attach. Details at http://www.caida.org/research/topology/as_core_network/.
[For details on a more sophisticated methodology for ranking AS interconnectivity, based on inferring AS relationships from BGP data, see http://www.caida.org/data/active/as-relationships/.]
Posted in Commentaries, IPv6, Topology, Updates, Visualization | No Comments »
July 31st, 2013 by kc
[Executive Summary from our annual report for 2012.]
This annual report covers CAIDA’s activities in 2012, summarizing highlights from our research, infrastructure, data-sharing and outreach activities. Our research projects span Internet topology, routing, traffic, economics, future Internet architectures, and policy. Our infrastructure activities continue to support measurement-based studies of the Internet’s core infrastructure, with focus on the health and integrity of the global Internet’s topology, routing, addressing, and naming systems. In 2012 we increased our participation in future Internet research in two dimensions: measuring and modeling IPv6 deployment; and an expanded role (in management) of the Named Data Networking project, one of the NSF-funded future Internet architecture projects headed into its third year. We also began a project to study large-scale Internet outages via correlation of a variety of disparate sources of data.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Commentaries, Updates | No Comments »
May 28th, 2013 by kc
I had the honor of presenting an overview of CAIDA’s recent research activities at the Network Mapping and Measurement Conference hosted by Sean Warnick and Daniel Zappala. Talks topics included: social learning behavior in complex networks, re-routing based on expected network outages along current paths, twitter data mining to analyze suicide risk factors and political sentiments (three different talks). James Allen Evans gave a sociology of science talk, an interview form of which seems to be achived by the Oxford Internet Institute. The organizers even arranged a talk from a local startup, NUVI, doing some fascinating real-time visualization and analytics of social network data (including Twitter, Facebook, Reddit, Youtube).
The workshop was held at Sundance, Utah, one of the most beautiful places I’ve ever been for a workshop. This workshop series was originally DoD-sponsored with lots of government attendees interested in Internet infrastructure protection, but sequester and travel freezes this year yielded only two USG attendees, and budget constraints may keep this workshop from happening again next year. I hope not, it was really a unique environment and exposed me to a range of work I would not otherwise have discovered anytime soon. Kudos to the organizers and sponsors.
Posted in Commentaries, Measurement, Updates | No Comments »
May 13th, 2013 by Alistair King and Alberto Dainotti
On March 17, 2013, the authors of an anonymous email to the “Full Disclosure” mailing list announced that last year they conducted a full probing of the entire IPv4 Internet. They claimed they used a botnet (named “carna” botnet) created by infecting machines vulnerable due to use of default login/password pairs (e.g., admin/admin). The botnet instructed each of these machines to execute a portion of the scan and then transfer the results to a central server. The authors also published a detailed description of how they operated, along with 9TB of raw logs of the scanning activity.
Online magazines and newspapers reported the news, which triggered some debate in the research community about the ethical implications of using such data for research purposes. A more fundamental question received less attention: since the authors went out of their way to remain anonymous, and the only data available about this event is the data they provide, how do we know this scan actually happened? If it did, how do we know that the resulting data is correct?
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Commentaries, Measurement, Security | 2 Comments »
April 19th, 2013 by kc
As part of our NSF-funded network research project on modeling Internet interconnection dynamics, David Clark (MIT) and I hosted the second Workshop on Internet Economics (WIE2012) last December 12-13. The goal of the workshop was to provide a forum for researchers, commercial Internet facilities and service providers, technologists, economists, theorists, policy makers, and other stakeholders to empirically inform emerging regulatory and policy debates. The theme for this year’s workshop was “Definitions and Data”. The final report describes the discussions and presents relevant open research questions identified by workshop participants. Slides presented at the workshop are available at the workshop home page. From the intro (but the full report (6-page pdf) is worth reading):
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Commentaries, Economics, Updates | No Comments »
April 15th, 2013 by Bradley Huffaker
[While getting our feet wet with D3 (what a wonderful tool!), we finally tried this analysis tidbit that’s been on our list for a while.]
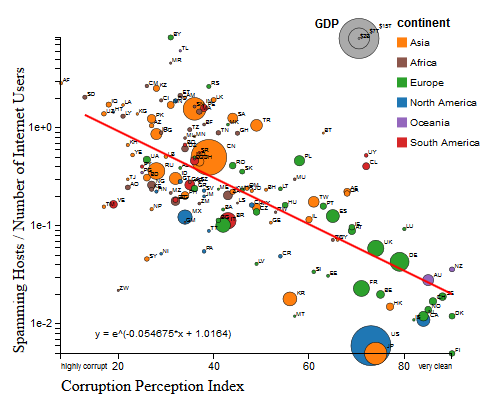
We recently analyzed the reputation of a country’s Internet (IPv4) addresses by examining the number of blacklisted IPv4 addresses that geolocate to a given country. We compared this indicator with two qualitative measures of each country’s governance. We hypothesized that countries with more transparent, democratic governmental institutions would harbor a smaller fraction of misbehaving (blacklisted) hosts. The available data confirms this hypothesis. A similar correlation exists between perceived corruption and fraction of blacklisted IP addresses.
For more details of data sources and analysis, see:
http://www.caida.org/research/policy/country-level-ip-reputation/
|
 |
 |
 |
x:Corruption Perceptions Index
y:IP population % |
x:Democracy Index
y:IP population % |
x:Democracy Index
y:IP infection % |
Interactive graph and analysis on the CAIDA website
Posted in Commentaries, Economics, Policy, Security, Visualization | 1 Comment »
January 22nd, 2013 by Robert Beverly
[This blog entry is guest written by Robert Beverly at the Naval Postgraduate School.]
In many respects, the deployment, adoption, use, and performance of IPv6 has received more recent attention than IPv4. Certainly the longitudinal measurement of IPv6, from its infancy to the exhaustion of ICANN v4 space to native 1% penetration (as observed by Google), is more complete than IPv4. Indeed, there are many vested parties in (either the success or failure) of IPv6, and numerous IPv6 measurement efforts afoot.
Researchers from Akamai, CAIDA, ICSI, NPS, and MIT met in early January, 2013 to firstly share and make sense of current measurement initiatives, while secondly plotting a path forward for the community in measuring IPv6. A specific objective of the meeting was to understand which aspects of IPv6 measurement are “done” (in the sense that there exists a sound methodology, even if measurement should continue), and which IPv6 questions/measurements remain open research problems. The meeting agenda and presentation slides are archived online.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Commentaries, Economics, Future, IPv6, Measurement, Topology, Updates | 3 Comments »
January 17th, 2013 by Karyn Benson
At the CoNEXT Student Workshop, in Nice, France on December 10, 2012, CAIDA shared recent research on Internet outages in a poster entitled “Gaining Insight Into AS-Level Outages through Analysis of Internet Background Radiation.”
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Commentaries, Measurement | No Comments »
December 5th, 2012 by Alistair King and Alberto Dainotti
On the 29th of November, shortly after 10am UTC (12pm Damascus time), the Syrian state telecom (AS29386) withdrew the majority of BGP routes to Syrian networks (see reports from Renesys, Arbor, CloudFlare, BGPmon). Five prefixes allocated to Syrian organizations remained reachable for another several hours, served by Tata Communications. By midnight UTC on the 29th, as reported by BGPmon, these five prefixes had also been withdrawn from the global routing table, completing the disconnection of Syria from the rest of the Internet.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Commentaries, International Networking, Internet Outages, Measurement, Security | No Comments »
December 4th, 2012 by Alberto Dainotti
Last week CAIDA researchers (Alberto and kc) visited National Harbor (Maryland) for the 1st NSF Secure and Trustworthy Cyberspace (SaTC) Principal Investigators Meeting. The National Science Foundation’s SATC program is an interdisciplinary expansion of the old Trustworthy Computing program sponsored by CISE, extended to include the SBE, MPS, and EHR directorates. The SATC program also includes a bold new Transition to Practice category of project funding — to address the challenge of moving from research to capability — which we are excited and honored to be a part of.
Read the rest of this entry »
Posted in Commentaries, Measurement, Security, Updates | No Comments »




